Introduction:
Males and females both are susceptible to developing colorectal cancer, which is one of the most prevalent forms of cancer worldwide. Even though it is rather common, there is frequently a lack of comprehension regarding this sickness and the consequences it carries. This article will provide you with an understanding of what colorectal cancer is, as well as its risk factors, symptoms, preventative techniques, and treatment choices that are currently available. Our goal is to better equip you with knowledge and awareness.
Understanding Colorectal Cancer:
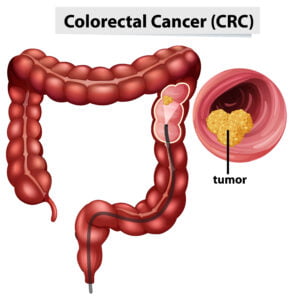
An Explanation of Colorectal Cancer The colon or the rectum, both of which are components of the digestive system, are the sites where colorectal cancer first manifests itself. The condition is typically caused by polyps, which are abnormal growths in the lining of the colon or rectum. If left untreated, polyps have the potential to develop into malignant growths over time. Although it is not always possible to determine the precise origin of colorectal cancer, several risk factors raise the likelihood of developing the disease.
Risk Factors:
- There is a correlation between age and the chance of developing colorectal cancer, with the majority of instances being diagnosed in people who are above the age of 50.
- An increased chance of developing colorectal cancer or polyps is associated with having a family history of either condition.
- Based on genetics, those who have Lynch syndrome or familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) are more likely to develop colorectal cancer than those who do not have these syndromes.
- Factors related to lifestyle include a diet that is high in red and processed meats, poor fiber intake, a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol use. All of these factors can lead to an elevated risk.
- The chance of acquiring colorectal cancer is increased in patients who suffer from inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which includes conditions such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis

Symptoms:
- It is possible that early-stage colorectal cancer would not display any apparent symptoms; therefore, screening is essential for the early discovery of the disease. The following are some of the common symptoms that may appear as the condition progresses:
- Constant discomfort in the abdomen region, such as cramping, flatulence, or actual pain
- Alterations in bowel habits. These may include diarrhea, constipation, or changes in the consistency of the stool.
- Blood in the feces or leaking from the rectal area
- Unexpected reduction in body mass
- Insufficiency or exhaustion
Prevention:
Although it is not possible to alter certain risk factors, such as age and family history, there are actions that individuals may take to lessen the likelihood of acquiring colorectal cancer. These include the following:
- Screening: Routine screening tests, such as colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, and fecal occult blood tests, can assist in the early detection of colorectal cancer or perhaps prevent the disease by locating and eliminating precancerous polyps.
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, which includes consuming a balanced diet that is abundant in fruits, whole grains, and vegetables, engaging in regular physical activity, preserving a healthy weight, reducing the amount of alcohol consumed, and avoiding smoking, can help reduce the chance of developing colorectal cancer.
- Get Familiar with Your Family’s Medical History Having an understanding of the medical history of your family and having a conversation about it with your healthcare practitioner will assist in determining the proper screening measures and assessing your risk.
- Medication: Certain drugs may be prescribed to persons who are at a high risk of developing colorectal cancer due to hereditary factors or their medical history to lower the risk of developing the disease.
Treatment:
Several criteria determine how colorectal cancer is treated. These factors include the stage of the cancer, the location of the cancer, and the individual’s overall health. Some of the most common treatment options are:
- Surgery: The primary therapy for colorectal cancer in its early stages is typically surgery, which involves the excision of the malignant tumor as well as any lymph nodes that are located nearby.
- Treatment with chemotherapy: Chemotherapy can be administered either before or after surgery to reduce the size of tumors, eliminate cancer cells, or stop the spread of cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy may be performed in conjunction with chemotherapy or surgery to eliminate cancer cells or to provide relief from symptoms.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy involves the use of medications that are specifically
designed to disrupt distinct pathways that cancer cells utilize to grow and spread.
Conclusion:
The condition known as colorectal cancer is a big health concern; yet, it is also a disease that is very treatable and preventative, particularly when it is found very early on. Individuals can take preventative measures to lessen their risk and maybe improve their results if they are diagnosed with the condition if they have a thorough grasp of the risk factors, symptoms, prevention techniques, and treatment options that are available. In the fight against colorectal cancer, it is important to keep in mind that regular screenings and keeping a healthy lifestyle are essential components. Always remember to prioritize your health, keep informed, and remain attentive.