Cancer Types
Oral Cancer
Oral Cancer is very common in Indian sub-continent because of the horrible habit of chewing Tobacco, Paan, Gutka etc. All these products are very very harmful as far as Oral Cancer is concerned. Oral Cancer can also be caused by innocuous things like Supari. Oral Cancer can affect the Teeth, Gums, Cheeks, Throat, Nose and all other parts of face.
Screening & Symptoms
Screening
Oral cancer screening helps detect early signs before symptoms appear. Dentists often perform these during routine check-ups by examining the mouth, tongue, and throat for any abnormal tissue or sores. For high-risk individuals, specialized imaging or biopsy may be recommended.
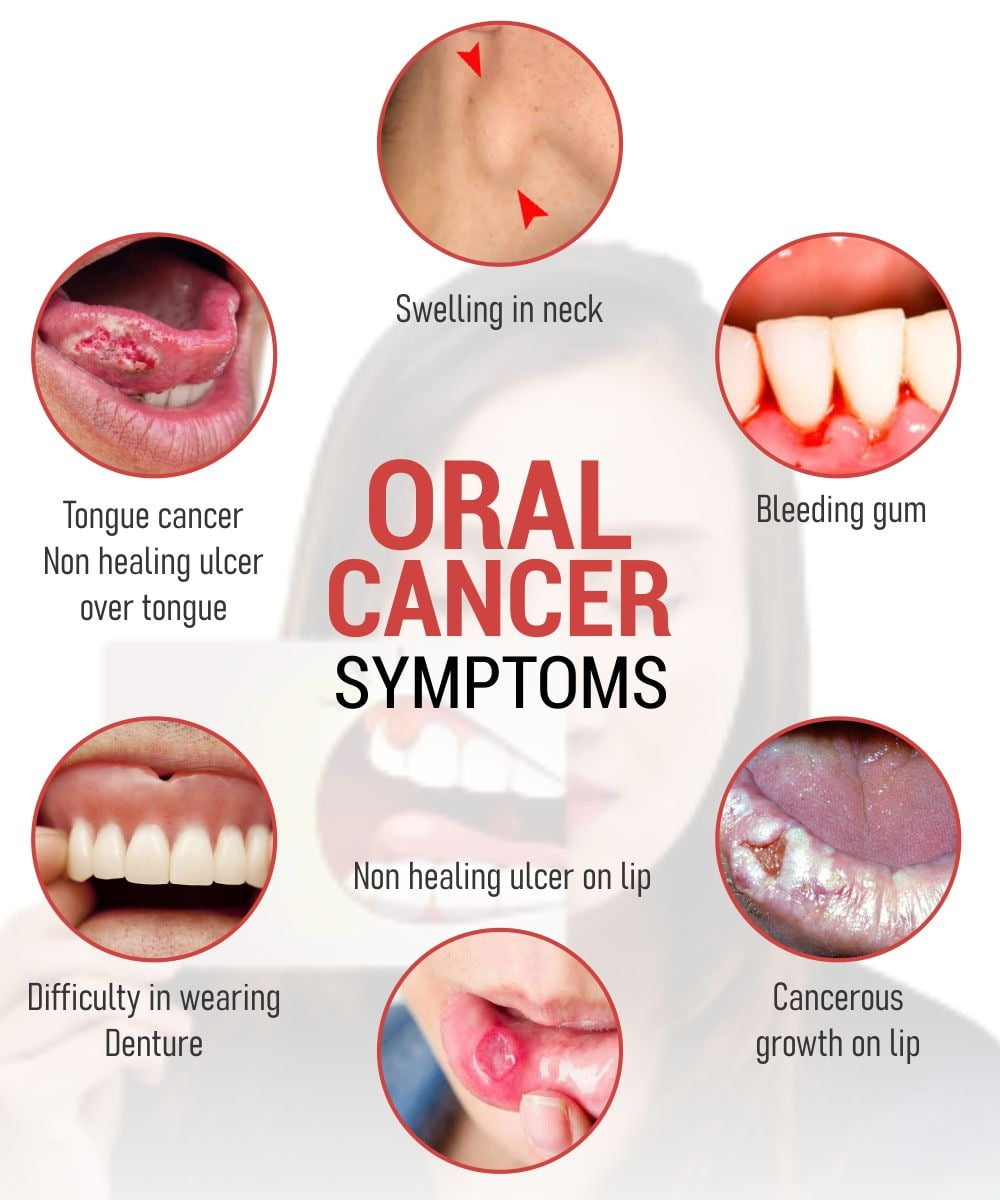
Symptoms
- Persistent mouth sores that do not heal
- Lumps or thickening in the cheek
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Red or white patches inside the mouth
- Persistent bad breath
- Unexplained bleeding
- Pain in the tongue or jaw
- Changes in voice
Treatment Modalities & Coping Treatment:
Treatment Modalities
Treatment options depend on the stage and location of the cancer. Common treatment modalities include:
- Surgery: To remove the tumor and affected tissues
- Radiation Therapy: Targeting cancer cells with high-energy rays
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that specifically target cancer cell mechanisms
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the immune system to fight cancer
Coping With Treatment
Cancer treatment can be physically and emotionally challenging. Support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals can make a significant difference. Counseling, nutrition planning, and stress management can also help improve quality of life during treatment.


Do's & Don'ts During Treatment
Do's:
- Follow your doctor’s dietary and care instructions
- Maintain hydration and a healthy diet
- Take prescribed medications regularly
- Attend all scheduled treatments and follow-ups
Don’ts:
- Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption
- Do not skip meals even if appetite is low
- Avoid exposure to infections, especially if your immune system is compromised
- Refrain from using over-the-counter products without consulting your doctor

Post Treatment Support, Followup Care and Surveillance :
Post-Treatment Support
After completing treatment, patients may need help with recovery. This could involve physical therapy, speech therapy, nutritional guidance, and emotional support. Joining cancer support groups can help survivors connect with others who share similar experiences.
Follow-ups Cancer Plan
Regular follow-up visits are essential to ensure the cancer has not returned and to monitor for any treatment side effects. These visits usually include physical exams, imaging, and blood tests.
Surveillance & Monitoring for Indications for Recurrence
Post-treatment, patients will need continuous monitoring to detect any signs of recurrence. This includes routine scans, self-examinations, and regular dental check-ups. Early detection of recurrence can improve the chances of successful treatment.
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Risk factors for oral cancer include tobacco use (smoking or chewing), excessive alcohol consumption, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, prolonged sun exposure (for lip cancer), a diet low in fruits and vegetables, a weakened immune system, and a family history of oral cancer
Early signs of oral cancer may include persistent mouth sores that do not heal, red or white patches in the mouth, a lump or thickening in the cheek, tongue, or throat, difficulty chewing or swallowing, persistent sore throat or hoarseness, and unexplained bleeding in the mouth.
Oral cancer is diagnosed through a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Your doctor may perform a thorough oral exam, including inspection of the mouth, throat, and neck. Biopsy, imaging tests (such as CT scans or MRI), and endoscopy may also be used to confirm the diagnosis and determine the stage of cancer.
While not all cases of oral cancer can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes and preventive measures can help reduce the risk. These include avoiding tobacco products, limiting alcohol consumption, practicing good oral hygiene, protecting the lips from sun exposure with lip balm or sunscreen, and getting vaccinated against HPV, particularly for individuals at higher risk. Regular dental check-ups can also aid in early detection and prevention of oral cancer.
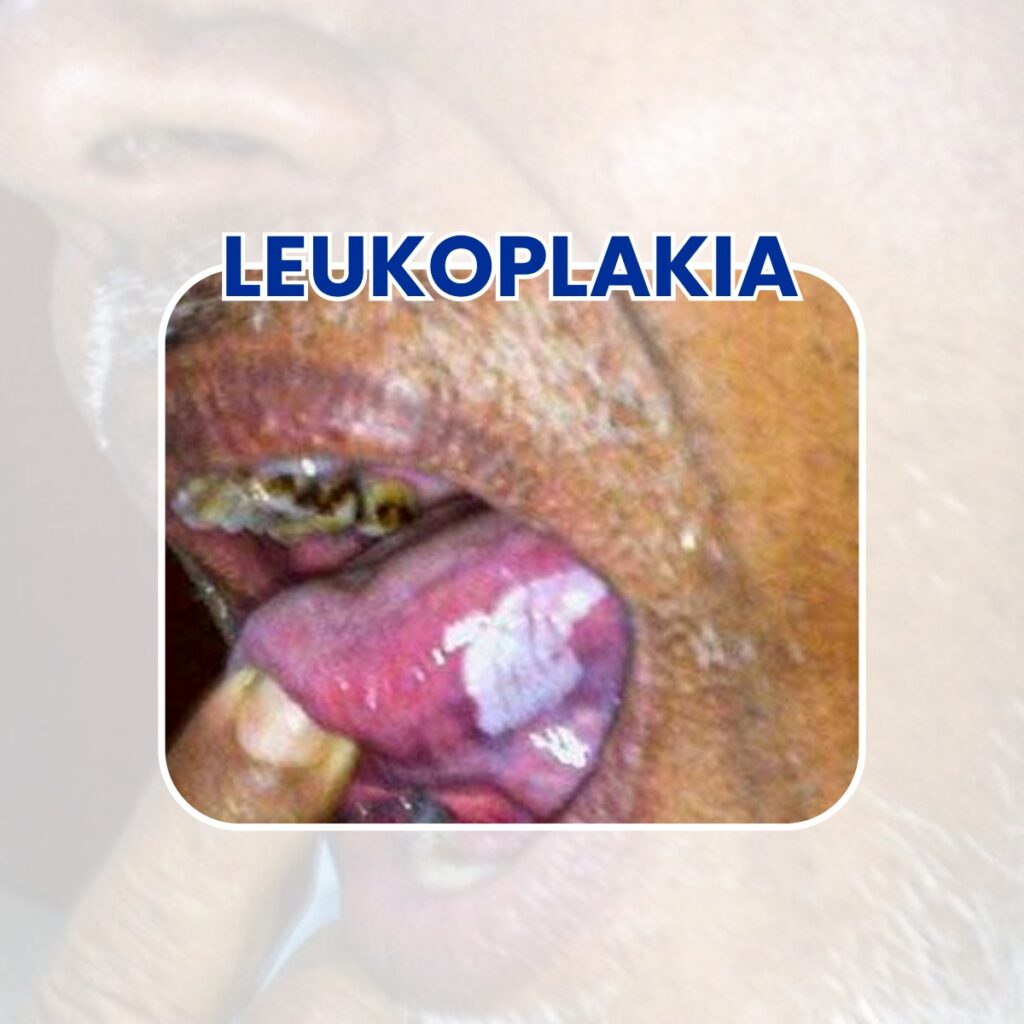
Leucoplakia
Leucoplakia is a condition characterized by white patches or lesions that develop on the mucous membranes inside the mouth, including the tongue, cheeks, gums, and the roof of the mouth. These white patches are often caused by chronic irritation or inflammation and can sometimes be a sign of early cancer or a precancerous condition. While not all leucoplakia cases progress to cancer, it’s essential to monitor and manage this condition closely. Here are some key points to consider:
- It has precancerous potential
- Risk Factors include tobacco use (smoking or chewing), heavy alcohol consumption
- Regular Monitoring should be done.
- Biopsy should be done if you have doubt.
- Treatment depends on various factors, including the size and location of the lesions and whether they show any signs of cancer.
- Prevention should be taken to avoid cancer.
- Early detection of leucoplakia and its management are essential for preventing the development of oral cancer.