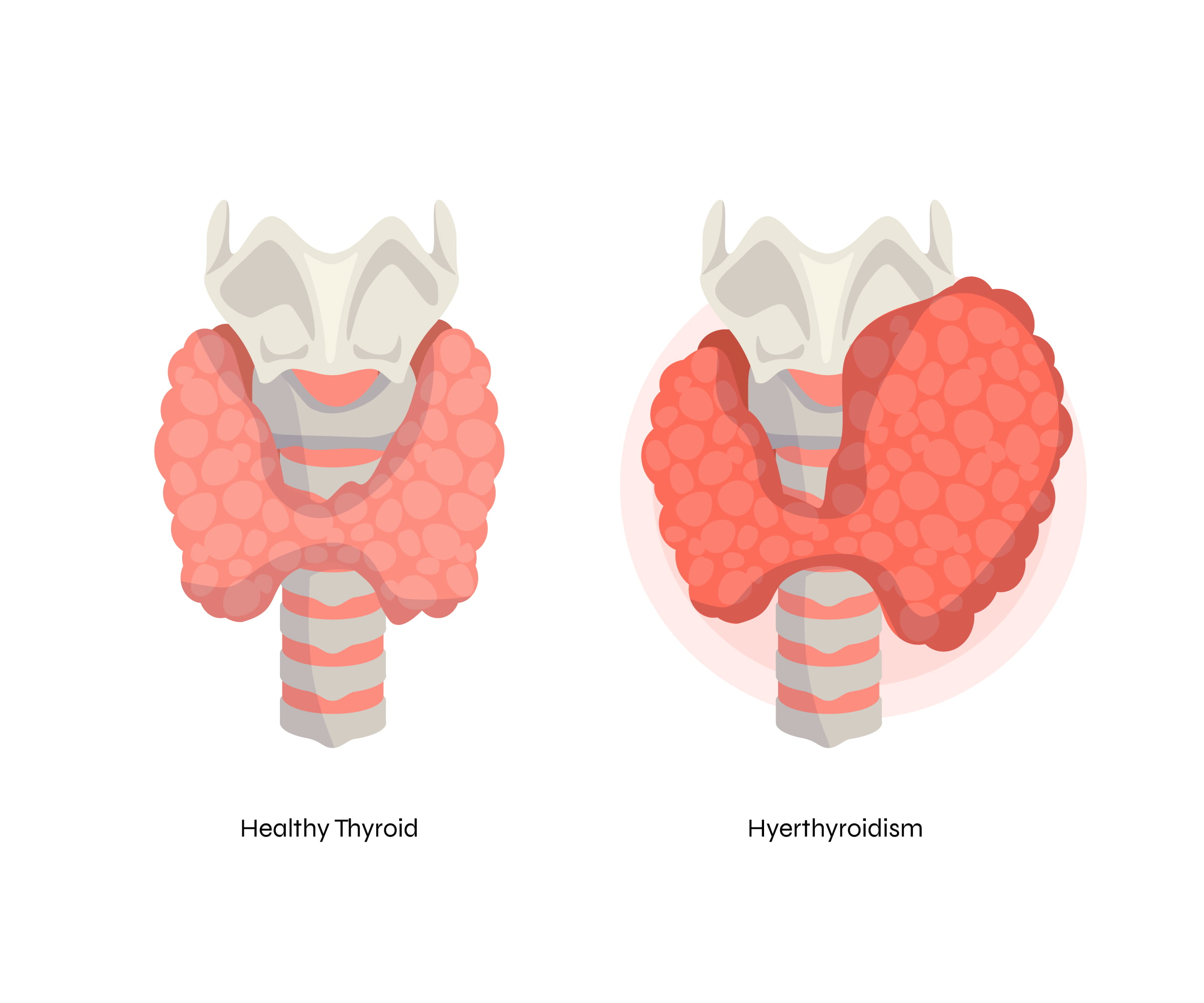
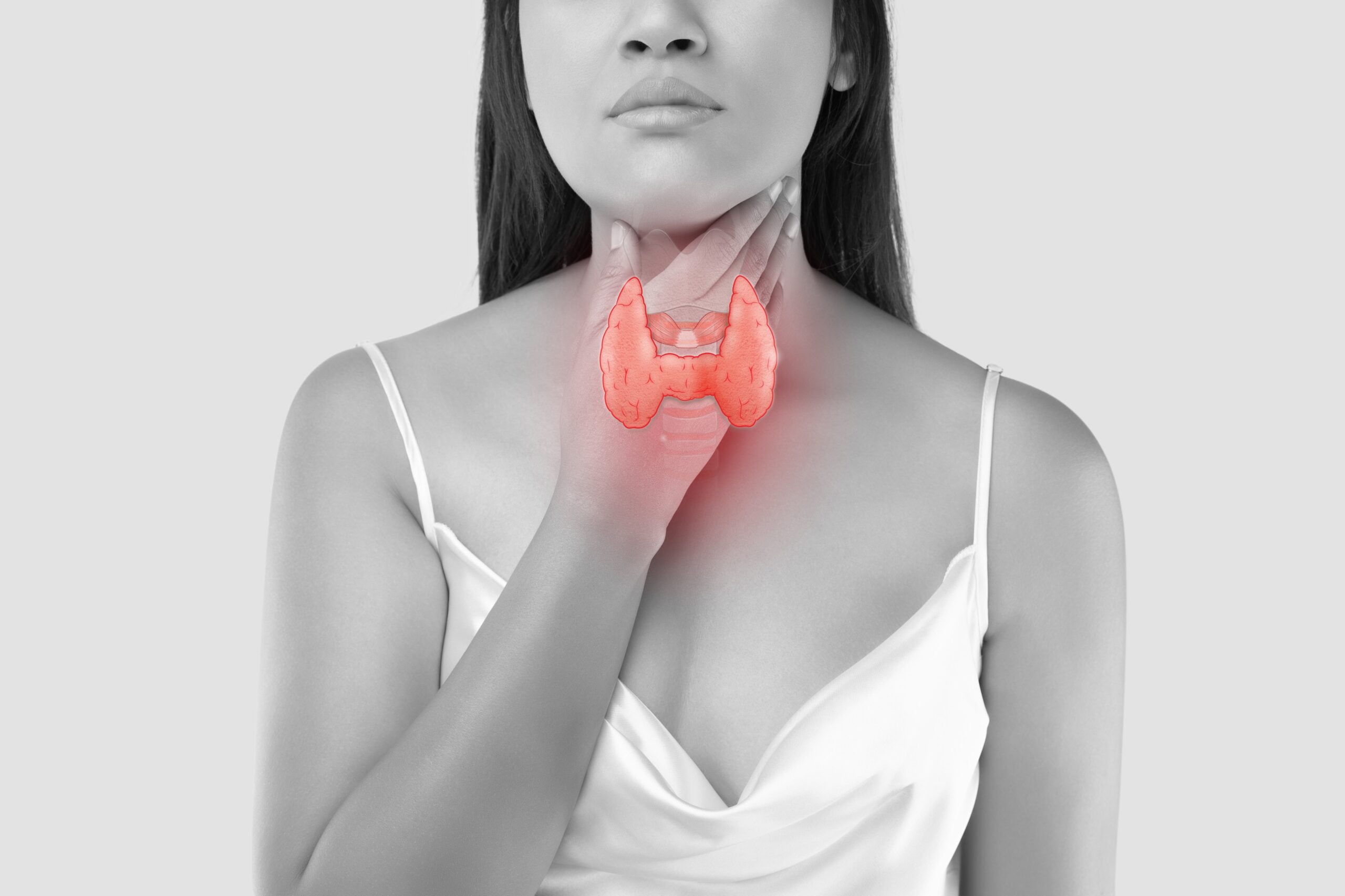
Treatment Modalities
Treatment options may include surgery (thyroidectomy), radioactive iodine therapy, thyroid hormone therapy, external beam radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Coping With Treatment
Coping strategies may involve seeking emotional support from loved ones or support groups, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing relaxation techniques, and adhering to treatment plans as prescribed by healthcare providers.