Cancer Types
Intestinal Cancer
Intestinal cancer refers to the development of malignant cells in the tissues of the intestines, which are crucial for digestion and nutrient absorption. It can affect various parts of the digestive system, including the small intestine and colon.
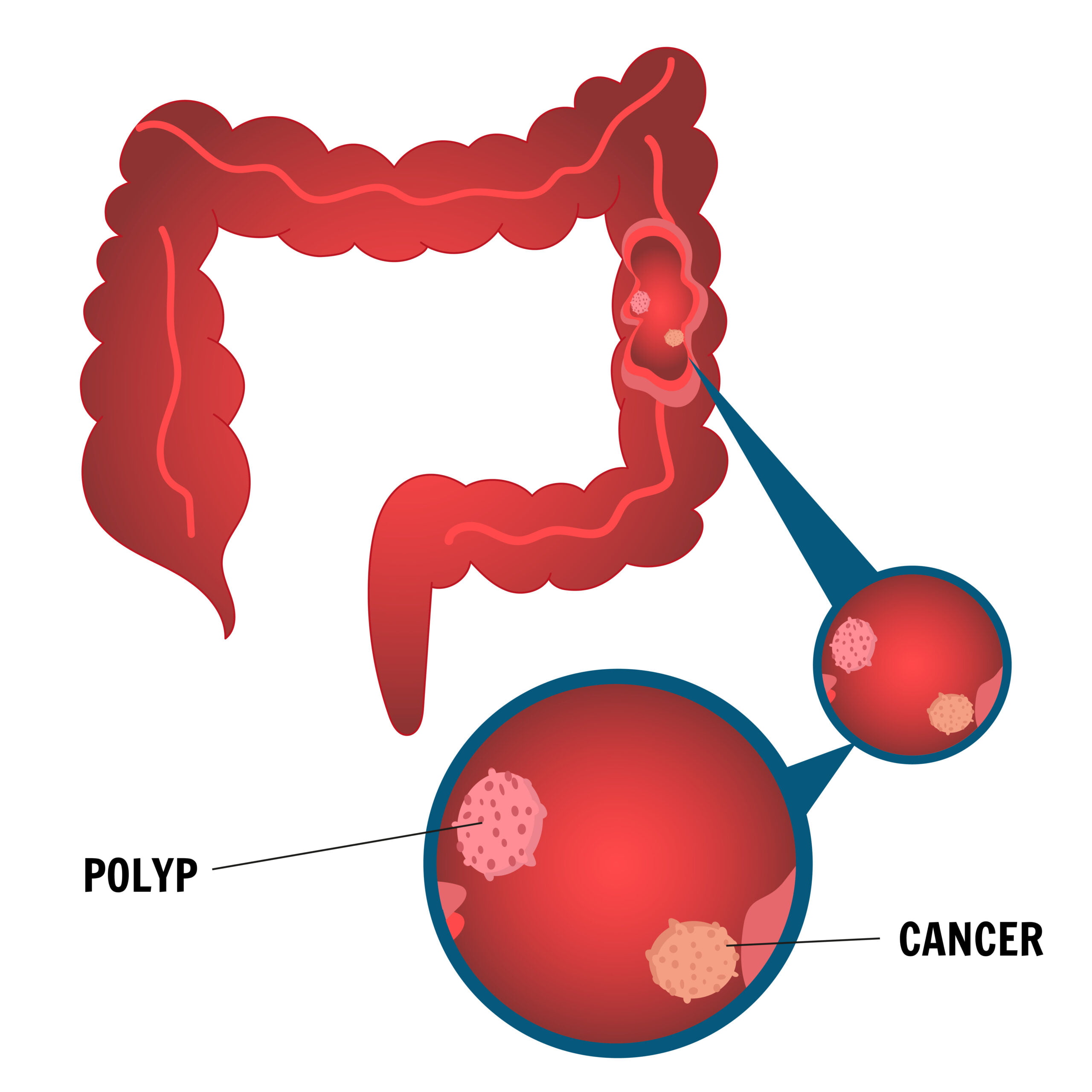

Risk Factors & Prevention
Risk Factors:
- Age
- Family history of intestinal cancer
- Personal history of colorectal polyps or inflammatory bowel disease
- Genetics
- Lifestyle factors (diet high in red or processed meats, low in fiber, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption)
Prevention:
- Regular exercise
- Healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Screening for early detection
- Limiting alcohol intake
- Avoiding tobacco products
Screening & Symptoms
Screening:
Regular screening, including colonoscopies and other imaging tests, is crucial for detecting intestinal cancer in its early stages when it's more treatable. Screening frequency may vary based on risk factors and age.
Symptoms & Signs:
- Persistent abdominal pain or discomfort
- Changes in bowel habits
- Blood in the stool
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Anemia


Diagnosis & Stages
Diagnosis:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Imaging tests (CT scans, MRIs)
- Colonoscopy
- Biopsy
Sub-types & Stages:
Intestinal cancer can be categorized into different sub-types (e.g., colorectal cancer) and stages (from stage I to IV) based on the extent of the disease and the involvement of nearby tissues or organs.
Treatment Modalities & Coping Treatment:
Treatment Modalities:
Treatment options for Intestinal cancer may include:
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Targeted therapy
- Immunotherapy
Coping With Treatment:
- Emotional support from friends, family, or support groups
- Counseling or therapy
- Integrative therapies like yoga or meditation
- Maintaining a positive outlook


Do's & Don'ts During Treatment
Do's:
- Follow the treatment plan as prescribed
- Communicate openly with healthcare providers
- Stay physically active as much as possible
- Eat a balanced and nutritious diet
Don'ts:
- Ignore symptoms or side effects
- Engage in activities that may compromise health
- Skip medications without consulting healthcare providers

Post Treatment Support, Followup Care and Surveillance :
Post Treatment Support:
- Survivorship programs
- Rehabilitation services
- Emotional and psychological support
- Regular follow-up appointments
Follow-ups Cancer Plan:
- Schedule regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers
- Monitor and manage potential side effects
- Stay informed about any changes in health status
- Adjust lifestyle as needed for optimal recovery.
Surveillance & Monitoring for Indications for Recurrence:
Regular surveillance through imaging tests and other monitoring methods to detect any signs of cancer recurrence early on.
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
While not entirely preventable, adopting a healthy lifestyle and participating in regular screenings can reduce the risk.
Side effects vary but may include fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and changes in appetite.
Screening frequency depends on risk factors and age, but regular screenings are crucial for early detection.
Some cases have a genetic component, and individuals with a family history should be vigilant and discuss screening options with their healthcare providers.
Adopting a healthy diet, staying physically active, and seeking emotional support can positively impact the treatment journey.
Integrative therapies like yoga or meditation may help with emotional well-being, but it's essential to consult healthcare providers before incorporating them.
Recovery varies based on the type of surgery and individual factors. Your healthcare team will provide personalized guidance.

