Treatment Modalities
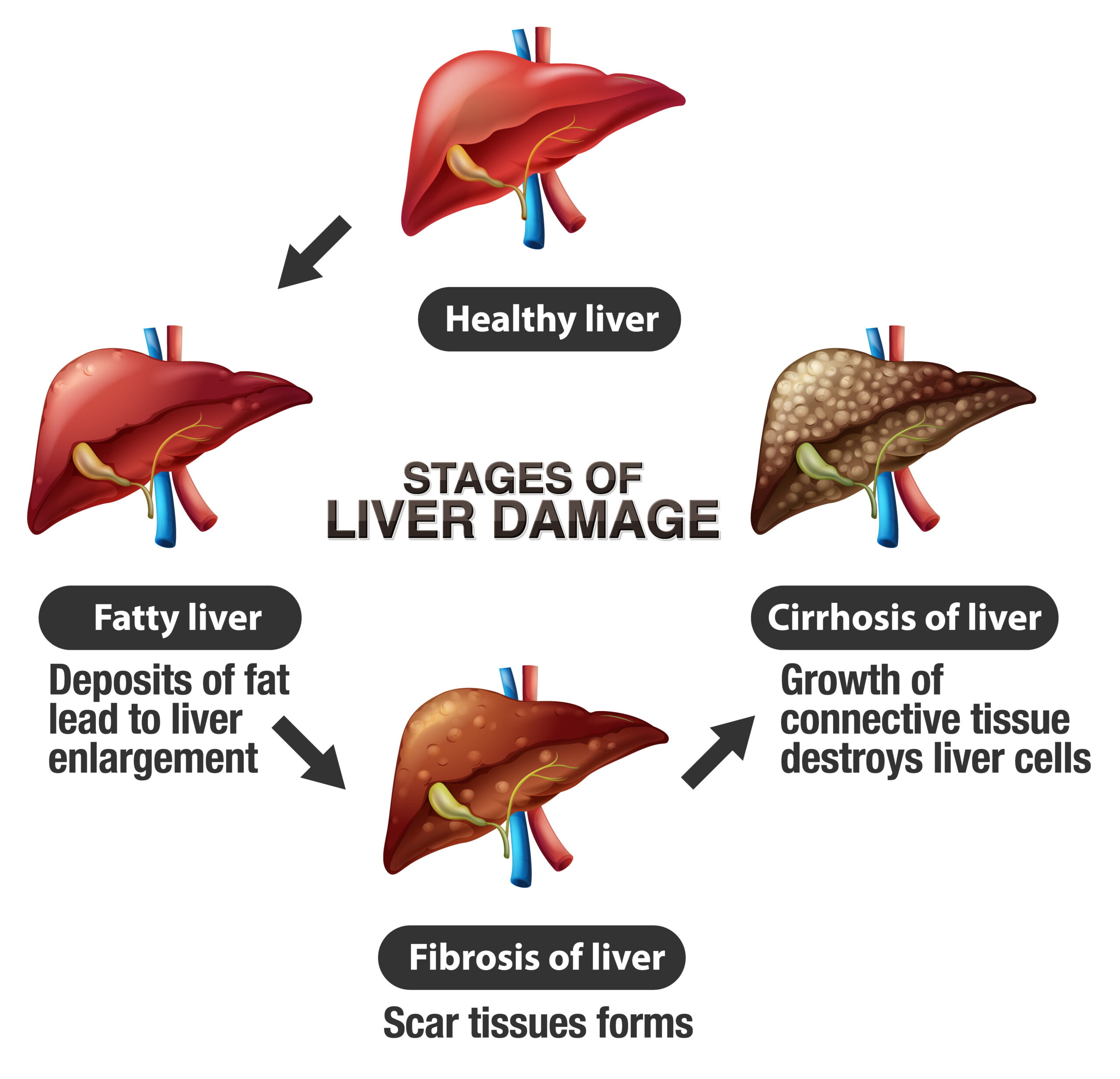
Treatment options vary based on the type and stage of liver cancer. Modalities may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. A personalized treatment plan is essential for optimal outcomes.
Coping With Treatment
Coping with liver cancer treatment involves emotional support, lifestyle adjustments, and maintaining a positive mindset. Support groups and counseling can be beneficial during this challenging time.